Table of Contents
- What is the MRCCA?
- Where do development restrictions apply?
- Whom do I contact about working in the MRCCA?
- Requirements applicable to the City of Minneapolis MRCCA
What (is the MRCCA)?
The Mississippi River Corridor Critical Area (MRCCA) is an area including lands adjacent to a 72-mile stretch of the Mississippi River extending through the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area. Land use and development within the MRCCA is regulated to protect the Mississippi River corridor’s natural, cultural, and scenic resources. Minnesota Statute 116G.15 establishes the authority for MRCCA Rules (Minnesota Rules 6106) that require the development of local (i.e., City) plans, ordinances, or other controls to implement MRCCA rules.
Where (do development restrictions apply):
The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources (DNR) maintains a map that illustrates the spatial extent of the MRCCA overlay. This information is also included in the City of Minneapolis zoning maps. MRCCA is further subdivided into the following districts located in Minneapolis based on land use:
- CA-RN (River Neighborhoods)
- CA-ROS (Rural and Open Space)
- CA-RTC (River Towns and Crossings)
- CA-SR (Separated from River)
- CA-UC (Urban Core)
- CA-UM (Urban Mixed)
As an overlay, standard zoning districts as defined by the City are also present. Within each MRCCA overlay district, additional requirements for land development, structure design, and erosion, vegetation, and stormwater management apply. Specific requirements vary according to the MRCCA district and the presence of Primary Conservation Areas. These areas include:
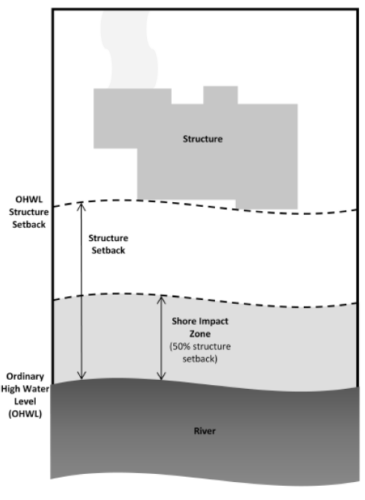
- Buff Impact Zone (BIZ) – The BIZ includes bluffs and land within 20 feet of bluffs. MN Rules 6106 defines bluffs as having a slope of 18 percent or greater and a rise of at least 25 feet.
- Shore Impact Zone (SIZ) – The SIZ is a strip of land extending from the ordinary high water level inland a distance of 50 percent of the required structure setback established for the underlying MRCCA district.
- Floodplains –Floodplains are areas adjoining waterbodies or watercourses that have or may be covered by regional floods. These areas have been mapped by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).
- Wetlands – Wetlands are transitional lands between terrestrial and aquatic systems where the water table is usually at or near the surface or land covered by shallow water.
- Native plant communities – These are plant communities of five acres or greater that meet the quality criteria established by the Minnesota Biological Survey to qualify as a native plant community.
- Significant existing vegetative stands – These are largely intact and connected plant communities that contain a sufficient representation of the original native plant community.
The spatial extent of each primary conservation area is detailed in the City’s MRCCA Plan. Compliance with applicable standards is determined through the City’s development review services (e.g., conditional use permits, site plan review, subdivisions, PUDs, variances, and other permits). Exemptions from MRCCA development standards are included in Chapter 551 of the City Code.
Whom (do I contact about working in the MRCCA):
The City of Minneapolis administers the MRCCA ordinance locally. Questions about projects located within the MRCCA should be direct to the City’s general help email and reference “Critical Overlay Area.” Inquiries will be forwarded to staff of the City’s Planning and Zoning department. The City performs site plan and other development reviews for MRCCA projects similar to other projects. The City also notifies the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources of all variance requests for setback requirements.
It is strongly encouraged that developers and property owners contact the City prior to submitting as land use application for property located in the MRCCA.
Requirements Applicable in the City of Minneapolis MRCCA:
Within the MRCCA overlay districts in Minneapolis, additional requirements apply to:
- Land Use and Land Development
- Structure Design and Placement
- Private Facilities
- Public Facilities
- Vegetation Management
- Land Alteration, Erosion Control, and Stormwater Management
Comprehensive requirements are included in Chapter 551 of the City Code.
Land Use and Land Development
Permitted land uses include those of the underlying zoning district.
Subdivisions, planned unit developments, and master-planned development or redevelopment of 5 acres or more, adjacent to the Mississippi River (or 5 acres or more for non-adjacent parcels), must meet the following development standards:
- Primary conservation areas must be designated as protected open space in quantities meeting the following as a percentage of total parcel area:
- CA-ROS District: 50 percent;
- CA-RN District: 20 percent;
- CA-RTC, CA-UM, and CA-UC District: 10 percent; and
- CA-SR District: 10 percent if the parcel includes native plant communities or provides feasible connections to a regional park or trail system (otherwise no requirement).
- If the primary conservation areas exceed protected open space requirements, then protection of native plant communities and natural vegetation in riparian areas shall be prioritized.
- If primary conservation areas exist but do not have natural vegetation, a vegetation assessment must be completed to evaluate the primary conservation areas and determine whether vegetation restoration is needed. If restoration is needed, vegetation must be restored according to MN Rules 6106.0150.
- If primary conservation areas do not exist on the parcel and portions of the parcel have been identified in the MRCCA plan as a restoration area, vegetation must be restored according to MN Rules 6106.0150 and the area must be designated as protected open space.
- Stormwater treatment areas or other green infrastructure may be used to meet the protected open space requirements if the vegetation provides biological and ecological functions.
- Land dedicated for public river access, parks, or other open space or public facilities may be counted toward the protected open space requirement.
- Protected open space areas must connect open space, natural areas, and recreational areas, where present on adjacent parcels, as much as possible to form an interconnected network.
- Designated open space areas must be permanently protected. Permanent protection methods must ensure the long-term management of vegetation to meet its biological and ecological functions, prohibit structures, and prohibit land alteration, except as needed to provide public recreational facilities and access to the river.
Activities exempt from the above land development standards for sites 5 acres or more adjacent to the Mississippi River (or 5 acres or more not adjacent to the Mississippi River) include:
- Minor subdivisions consisting of three or fewer lots;
- Minor boundary line corrections;
- Resolutions of encroachments;
- Additions to existing lots of record;
- Placement of essential services; and
- Activities involving river-dependent commercial and industrial uses.
Structure Design and Placement
- Lot Size – Lot size shall be governed by the underlying zoning district.
- Building Height – Building height shall generally be governed by the underlying zoning district but shall not exceed the maximum presented in Table 1.
- Setbacks – Setbacks shall generally be governed by the underlying zoning district but shall not exceed the maximum presented in Table 1.
- Structure Placement
- No structures may be placed in the BIZ or SIZ unless exempted per MN Rules 6106.0180
- Limitations on structures per the city’s floodplain, shoreland, and wetland ordinances still apply.
- Lateral expansion of non-conforming principal structures may be permitted provided they do not expand further into required setbacks from the river and bluff.
- Line of Sight – the development or expansion of structures shall be placed to preserve the view of the river corridor from other properties on both sides of the river and by the public.
- Exemptions – Exemptions to setback, building height, and structure location requirements are detailed in City Code Chapter 551.
- Built Form Guidance – The Built Form categories of the City’s comprehensive plan guide the scale of development for every parcel in the city, independent of the uses allowed on the site. The built form of all new and remodeled buildings must be consistent with the guidance of the Built Form Map and MRCCA district requirements. The built form districts are described below and are mapped in Figures 2-5 through 2-7 of City’s MRCCA Plan.
| Build & Construction Standards | Rural Open Space (CA-ROS) | River Neighborhood (CA-RN) | River Towns and Crossings (CA-RTC) | Separated from River (CA-SR) | Urban Mixed (CA-UM) | Urban Cores (CA-UM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Structure Height | 35′ | 35′ | 48’* | Underlying Zoning | 65’* | Underlying Zoning |
| Mississippi River Structure Setback | 200′ | 100′ | 75′ | n/a | 50′ | Underlying Zoning |
| Bluff Structure Setback | 100′ | 40′ | 40′ | 40′ | 40′ | 40′ |
* Tiering of structures away from the Mississippi River and from blufflines must be is given priority, with lower structure heights closer to the river and bluff lines; greater height may be allowed via conditional use permit, see City Code Chapter 551.
Private Facilities
- Private roads, driveways, and parking — Except as exempted per MN Rules 6106.0180, these facilities must:
- Be designed to take advantage of natural vegetation and topography to preserve views.
- Comply with structural setbacks according to the MRCCA District.
- Not be placed in the BIZ or SIZ (unless exempt per MN Rules 6106.0180).
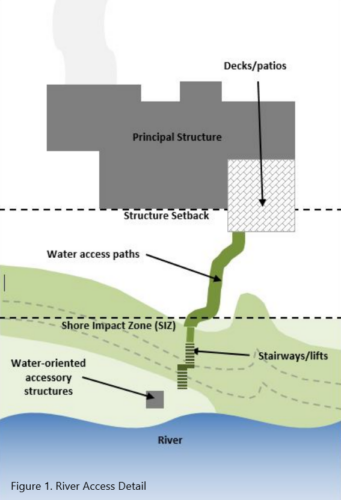
- Private water access and viewing
- Access paths must be no more than 8 feet wide in the SIZ and 4 feet wide in the BIZ.
- Access ramps must comply with MN Rules 6115.0210 and the Design Handbook for Recreational Boating and Fishing Facilities.
- Stairways and lifts must not exceed four feet in width on residential lots. Landings for stairways and lifts on residential lots must not exceed 32 square feet in area.
- Canopies or roofs are prohibited on stairways, lifts, or landings.
- Stairways, lifts, and landings must be located in the least visible portion of the lot whenever practical.
- Ramps, lifts, mobility paths, or other facilities for persons with physical disabilities are allowed for achieving access to shore areas.
- Accessory structures — One water-oriented accessory structure is allowed for each riparian lot or parcel less than 300 feet in width at the ordinary high water level, with one additional water-oriented accessory structure allowed for each additional 300 feet of shoreline on the same lot or parcel. Water-oriented accessory structures are prohibited in the BIZ and must:
- Not exceed 12 feet in height.
- Not exceed 120 square feet in area.
- Be placed a minimum of 10 feet from the ordinary high water level.
- Decks and patios in setback areas — decks and patios may encroach minimum setback distances if they meet other applicable criteria and satisfy the following:
- Encroachment of deck or patio does not exceed 15% of the structure setback.
- Total deck/patio area is no more than 25% of total area within the 15% allowable encroachment.
- The deck/patio does not extend into the BIZ.
Public Facilities
- General design standards — All public facilities must be designed and constructed to:
- Minimize visibility of the facility from the river to the extent consistent with the purpose of the facility and comply with structure design and placement standards.
- Be consistent with the vegetation management standards, erosion control, and storm water management standards.
- Avoid primary conservation areas, unless no alternative exists. If no alternative exists, then disturbance to primary conservation areas must be avoided to the greatest extent practicable.
- Minimize disturbance of fish and wildlife spawning and nesting times.
- Facility-specific standards are also applicable per MN Rules 6106.0130 for the following:
- Right-of-way maintenance.
- Crossings of public waters or public land.
- Public utilities.
- Public transportation facilities.
- Public recreational facilities.
Exterior Lighting
- External lighting standards are applicable within the MRCCA per City Code Chapter 551 as follows:
- Luminaires must be full-cutoff or fully shielded.
- Uplighting is not permitted.
- For structures other than single-, two-, and three-family dwellings architectural accent, ornamental, or decorative lighting is not permitted, unless otherwise allowed by conditional use permit.
Conditional use permits and exemptions are detailed in City Code Chapter 551
Vegetation Management
Vegetation management restrictions apply to primary conservation areas including the BIZ, SIZ, areas within 50 feet of a wetland or natural drainage route, areas of native plant communities, and significant existing vegetative stands. Generally, a permit is required for vegetation management within these areas; a vegetation restoration plan consistent with MN Rules 6106.0150 is required with the permit and for subdivision planning.
- General vegetation standards:
- Development is sited to minimize removal of or disturbance to natural vegetation.
- Soil, slope stability, and hydrologic conditions are suitable for the proposed work as determined by a professional engineer.
- Clearing is the minimum necessary and designed to blend with the natural terrain and minimize visual impacts to public river corridor views and other scenic views.
- To the extent possible, trees with a diameter at breast height of 12 inches or larger shall be preserved.
- Vegetation removal activities are conducted so as to expose the smallest practical area of soil to erosion for the least possible time, and to avoid bird migration and nesting seasons.
- Where there is no feasible or prudent alternative to cutting trees on a site, tree density and ground cover should be restored to native vegetation appropriate to the ecology of the site
- Activities allowed with a vegetation permit:
- Clearing of vegetation that is dead, diseased, dying, or hazardous
- Clearing to prevent the spread of diseases or insect pests
- Clearing to remove invasive non-native species.
- Clearing to prepare for restoration and erosion control management activities
- The minimum necessary for development that is allowed with a building permit
- Activities allowed without a vegetation permit:
- Maintenance of existing lawns, landscaping and gardens.
- Removal of vegetation in emergency situations as determined by the city.
- Right-of-way maintenance for public facilities.
- Selective vegetation removal, provided that vegetative cover remains consistent with the management purpose of the MRCCA District, including removal of:
- Vegetation that is dead, diseased, dying, or hazardous;
- Vegetation to prevent the spread of diseases or insect pests; and
- Invasive non-native species.
Land Alteration, Erosion Control, and Stormwater Management
Land alteration within the BIZ is generally prohibited; erosion control, repair and maintenance of existing facilities, and minimum activity necessary for land uses exempted per MN Rules 6106.0180 are allowed by permit.
Erosion Control
- Construction, repair, or replacement of rock riprap, retaining walls, and other erosion control structures located at or below the OHWL must comply with applicable parts of MN Rules 6115.0215 and may not proceed until applicable permits are obtained.
- Erosion protection measures should make maximum use of natural in-place vegetation and additional planting of new native vegetation rather than the use of artificial devices on site as erosion control measures.
- Development shall minimize runoff and should not cause erosion, increase the net surface runoff rate, or decrease the net rate of storm water absorption on the site.
- Adequate erosion protection measures shall be used to ensure that soil loss levels do not degrade the receiving water body.
- The MPCA Stormwater Manual shall be used as a guide for construction site best management practices.
- Artificial devices such as retaining walls should be allowed only as a last resort after consideration of all other best management practices such as native vegetative or bioengineering solutions to minimize slope and erosion problems.
- The size and extent of erosion control structures shall be the minimum necessary to correct the erosion problem and meet the following limits, unless determined necessary by a professional engineer:
- Retaining walls must not exceed 5 feet in height and must be placed at least 20 feet apart.
- Riprap must not exceed the height of the regulatory flood protection elevation.
- Repair of existing rock riprap, retaining walls, and other erosion control structures above the ordinary high water level does not require a permit provided it does not involve any land alteration.
Stormwater Management
- Stormwater management facilities are generally prohibited in the BIZ but may be allowed by permit if:
- There are no alternatives for stormwater treatment outside the BIZ.The site is designed to reduce runoff reaching the BIZ to the greatest extent practicable.
- The construction and operation of the facility does not affect slope stability.
- There are no alternatives for storm water treatment outside the BIZ.
- The site is designed to reduce runoff reaching the BIZ to the greatest extent practicable.
- The construction and operation of the facility does not affect slope stability.
- Mitigation based on the best available engineering and geological practices is applied to eliminate or minimize the risk of slope failure.
- Multipurpose trails and sidewalks triggering a city permit are exempt from a stormwater permit if there is down gradient vegetation or a filter strip that is at least 5 feet wide.
- Outside of the BIZ, SIZ, and in areas more than 50 feet from the OHWL, wetlands, and natural drainage ways, storm water runoff must be directed away from the bluff impact zones or unstable areas.
- Stormwater management practices within the MRCCA must meet applicable city stormwater requirements and MWMO performance standards.
Development on Steep Slopes
- Construction of structures, impervious surfaces, land alteration, vegetation removal, or other construction activities are allowed on steep slopes if:
- Development can be accomplished without increasing erosion or runoff.
- The soil types and geology are suitable for the proposed development; and
- Vegetation is managed according to the requirements MN Rules 6106.0150.